What is Robotic Surgery of the GI Tract?
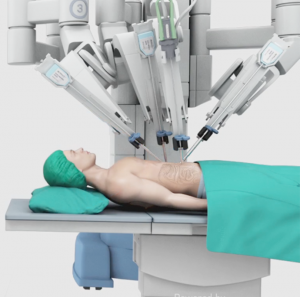
Robotic surgery is a minimally invasive surgery that is performed by your surgeon with the help of robotic arms that hold and manipulate the special surgical instruments. Gastrointestinal (GI) conditions occur due to structural and functional abnormalities of the stomach and intestine. Many GI conditions can be treated with robotic surgery.
The da Vinci Robotic Surgical System is a widely employed robotic system used to perform surgical procedures. It consists of a surgeon’s computer console, a patient-side cart with four interactive robotic arms, a high-performance vision system (3D camera) and miniaturized surgical instruments.
Indications
Robotic surgery of the GI tract is indicated for GI conditions such as:
- Acid reflux (GERD)
- Crohn’s disease
- Diverticulitis
- Ulcerative colitis
- Fistulas
- Hiatal hernia
- Rectal prolapse
- Cancer of the stomach, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, colon, adrenal gland and spleen
Am I a Candidate for Robotic Surgery?
The decision to undergo robotic surgery depends on your health condition and your doctor’s preference. Robotic surgery is contraindicated in patients with bleeding disorders, severe obesity, pregnancy, cirrhosis, bowel obstruction, cardiopulmonary diseases such as COPD and adhesions from previous abdominal surgery. Discuss with your doctor about all treatment options suitable for you, including robotic surgery.
Preparing for the Surgery
- Your doctor will assess your symptoms and perform a physical exam.
- Your doctor will take your medical history and may order imaging tests such as X-ray, CT-scan or MRI. Certain blood tests may also be ordered.
- Your doctor will discuss with you about the medicines you are taking and those you should stop taking prior to the procedure. Inform your doctor if you are allergic to any medicines or anesthesia.
- Colonoscopy may be required to diagnose colon conditions which use a thin tube-like device fitted with a camera to view the inside of your colon.
- Your doctor may order capsule endoscopy. For this procedure, you consume a capsule containing a tiny camera (passed out in stools). The pictures obtained are used in diagnosis.
- Further, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the GI condition.
Robotic Surgery of the GI Tract
The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia and includes the following steps:
- The surgical area is cleaned with an antiseptic solution.
- A few small incisions are made over the surgical site.
- A powerful camera and miniature robotic instruments are inserted through the incisions.
- Your surgeon views high-definition 3D images of internal organs while sitting at the console.
- The robotic instruments are controlled and manipulated by your surgeon to perform the surgical procedure.
- Special robotic instruments are used to perform internal stitches.
- The incisions are then closed, and a bandage is applied.
Risks and Complications
Complications are rare when the surgery is performed by an experienced surgeon. However, as with any surgery, complications may occur. Some of the complications can include damage to nearby organs, nerves and blood vessels, infection, reaction to anesthesia, and bleeding.
Advantages
Robotic surgery of the GI tract is beneficial compared to conventional surgery. The advantages include:
- Less pain
- Tiny surgical scars
- Short hospital stay
- Minimum blood loss
- Minimum risk of infection
- Quick recovery
Other General Surgery Procedures
- Laparoscopic/Robotic Hernia Repair
- Laparoscopic/Robotic Cholecystectomy
- Laparoscopic/Robotic Fundoplication for Acid Reflux
- Robotic LINX Procedure for Acid Reflux
- Laparoscopic/Robotic Splenectomy
- Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF)
- Laparoscopic/Robotic Colon Resection
- Laparoscopic/Robotic Colon Resection for Diverticulitis
- Laparoscopic/Robotic Heller Myotomy for Achalasia
- Laparoscopic/Robotic Adrenalectomy
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy
- Upper Endoscopy
- Gastrointestinal Conditions








